A single-stage amplifier circuit is shown in Figure 15. The
amplifier consists of a transistor, the circuit for matching the source termination and
the transistor, and that for matching the load
termination and the transistor. The biasing circuit is ignored for brevity. The source and load
terminations are usually 50 ![]() . The function of the matching
circuits is to provide suitable source and load conditions for the transistor
such that the transistor can generate power gain for the input signal under a
stable condition.
. The function of the matching
circuits is to provide suitable source and load conditions for the transistor
such that the transistor can generate power gain for the input signal under a
stable condition.
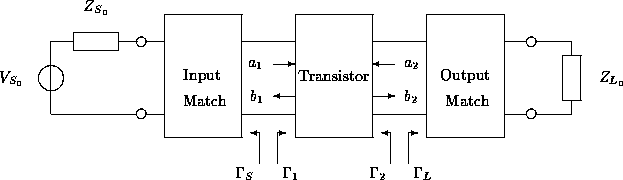
Figure 15: Small-signal high-frequency amplifier
Note that ![]() is the input reflection coefficient of the amplifier when output port
is connected to the load with a reflection coefficient of
is the input reflection coefficient of the amplifier when output port
is connected to the load with a reflection coefficient of ![]()
![]()
Similarly, ![]() is the output reflection coefficient of the amplifier when input port
is connected to the source with a reflection coefficient of
is the output reflection coefficient of the amplifier when input port
is connected to the source with a reflection coefficient of ![]()
![]()
![]()
The amplifier can be simplified to the network shown in Figure 16. Note that the network can be represented by the flow graph in Figure 13 if S-parameter is used to model the transistor.
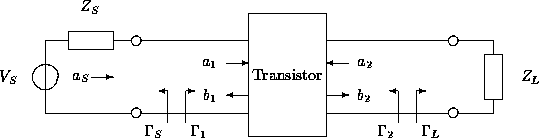
Figure 16: Simplified amplifier network